Medical laboratories play a critical role in the diagnosis and treatment of various diseases. However, with the increasing complexity of laboratory tests and the volume of samples processed each day, there is a growing need for reliable and efficient methods of tracking medical samples.
Backward traceability of medical samples is one such method that ensures patient safety and quality assurance.
Backward traceability in the context of healthcare refers to the ability to track a medical sample to its source. In other words, it is the ability to track the processing steps of a sample from the final diagnosis back to the time and location of the initial tissue collection.
Why Backward Traceability Matters
Once a tissue sample has been cut into thin sections, stained, and examined under a microscope, it cannot be reassembled into its original form. The only way from there is forward.
Therefore, it is essential to maintain a complete record of the sample’s journey through the lab to ensure that all steps of the testing process are accurately documented. And whenever the need arises, the processed samples can be traced backward.
From a management perspective, this information is critical for several reasons:
Quality assurance
Quality assurance is a critical component of any laboratory’s operations, and backward traceability is an essential part of this process. By tracing the source of any errors or discrepancies, laboratories can identify the root cause of the problem and take corrective action to prevent similar issues in the future.
For example, if a sample is mislabeled, and the lab fails to identify the error, it could result in incorrect test results. Backward traceability ensures that the source of the error is identified, and corrective action is taken to prevent similar mistakes in the future. In this way, backward traceability plays a crucial role in maintaining the quality and reliability of laboratory testing.
Patient safety
Accurate identification and tracking of medical samples are crucial for ensuring that patients receive the correct diagnosis and treatment. If a sample is mislabeled, lost, or contaminated, it can lead to inaccurate test results, incorrect diagnosis, and ultimately, compromised patient care.
For instance, if a patient receives an incorrect diagnosis or treatment due to errors in the laboratory’s testing process, it can have serious consequences for their health. Backward traceability minimizes the risk of errors in the lab and ensures patient safety.
Regulatory compliance
Laboratories must comply with strict regulations and guidelines set by various agencies. Backward traceability is a critical component of compliance and ensures that laboratories meet the necessary standards for quality control and assurance.
For example, the CAP requires that laboratories maintain complete and accurate records of sample collection, processing, and testing. Backward traceability ensures that these records are maintained and easily accessible, which helps laboratories to comply with regulatory requirements.
How to Achieve Backward Traceability
According to an article published by Medical Lab Management, Histology Specimen goes through the following steps:
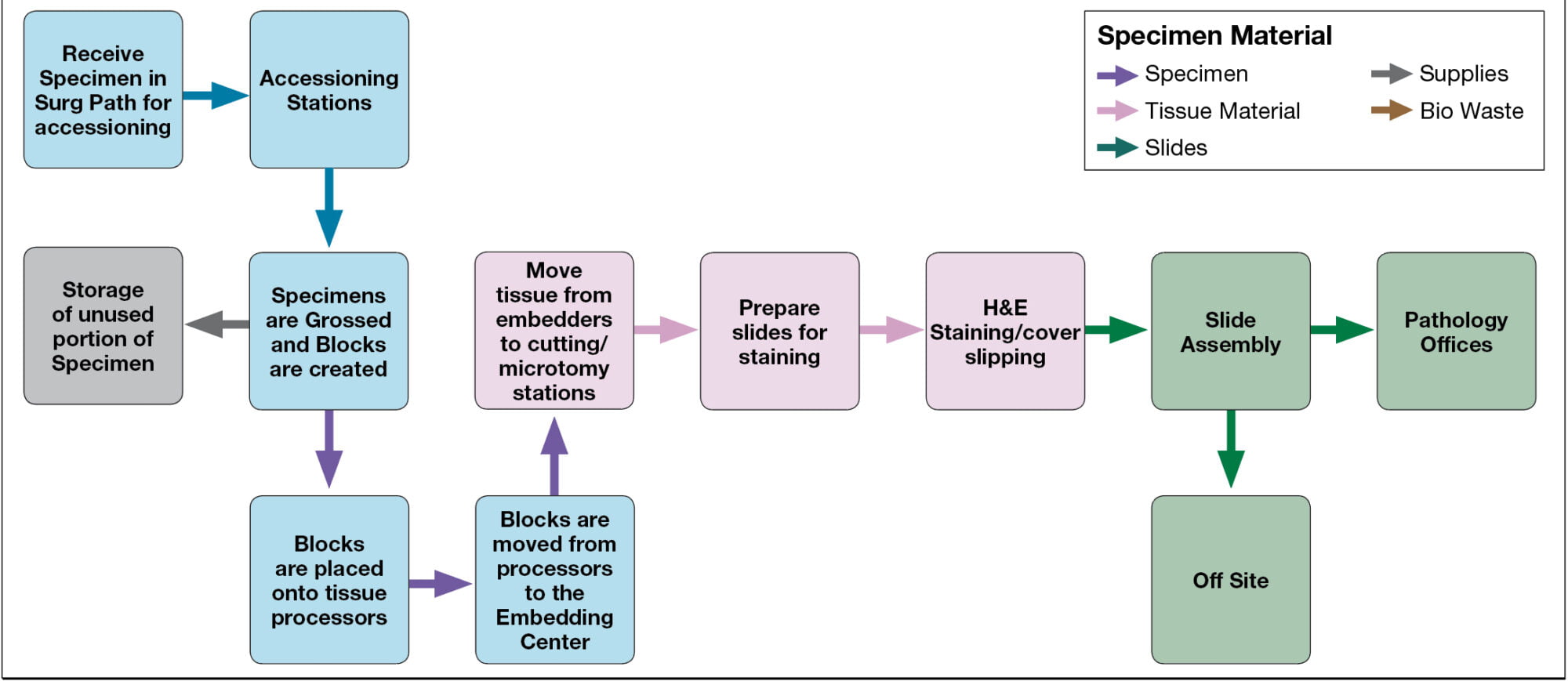
In such a context, backward traceability begins with the labeling and identification of the sample/specimen. Each sample must be assigned a unique identifier, such as a barcode, that links it to the patient and the order information. This information is recorded in the laboratory information system (LIS), which tracks the sample throughout the testing process.
As the sample moves through the laboratory, each step is documented in the LIS, including the date and time of collection, receipt, testing, and result reporting. This information is linked to the unique identifier, allowing laboratories to trace the sample back to its source and identify any potential issues or errors.
Therefore, to achieve backward traceability, pathology labs must implement a comprehensive and well-designed sample tracking system that ensures that each sample is accurately identified, processed, tested, and reported while maintaining a complete record of its journey through the lab.
The following are the steps necessary to implement a sample tracking system:
1. Develop Clear Protocols
Developing clear protocols is essential to ensure that everyone in the lab is on the same page and follows the same procedures. Clear protocols for sample collection, transportation, processing, testing, reporting, and storage, as well as the chain of custody, should be established and followed rigorously.
2. Standardize Record-Keeping Procedures
Standardized record-keeping procedures ensure that every piece of information about the sample is recorded accurately and completely.
For traceability, a standardized method of recording information about the sample, such as the patient’s name, identification number, and the date and time of collection, should be established. Additionally, the lab can establish clear procedures for recording the results of each test performed, including who performed the test, when it was performed, and what equipment was used.
3. Implement a Secure Database or Electronic System
A secure database or electronic system is an essential component of an effective sample tracking system. It should be used to store all information about the sample, including the patient’s medical record, test results, and any associated documentation. The database should be secure, easily accessible, and have clear protocols for data entry, modification, and backup.
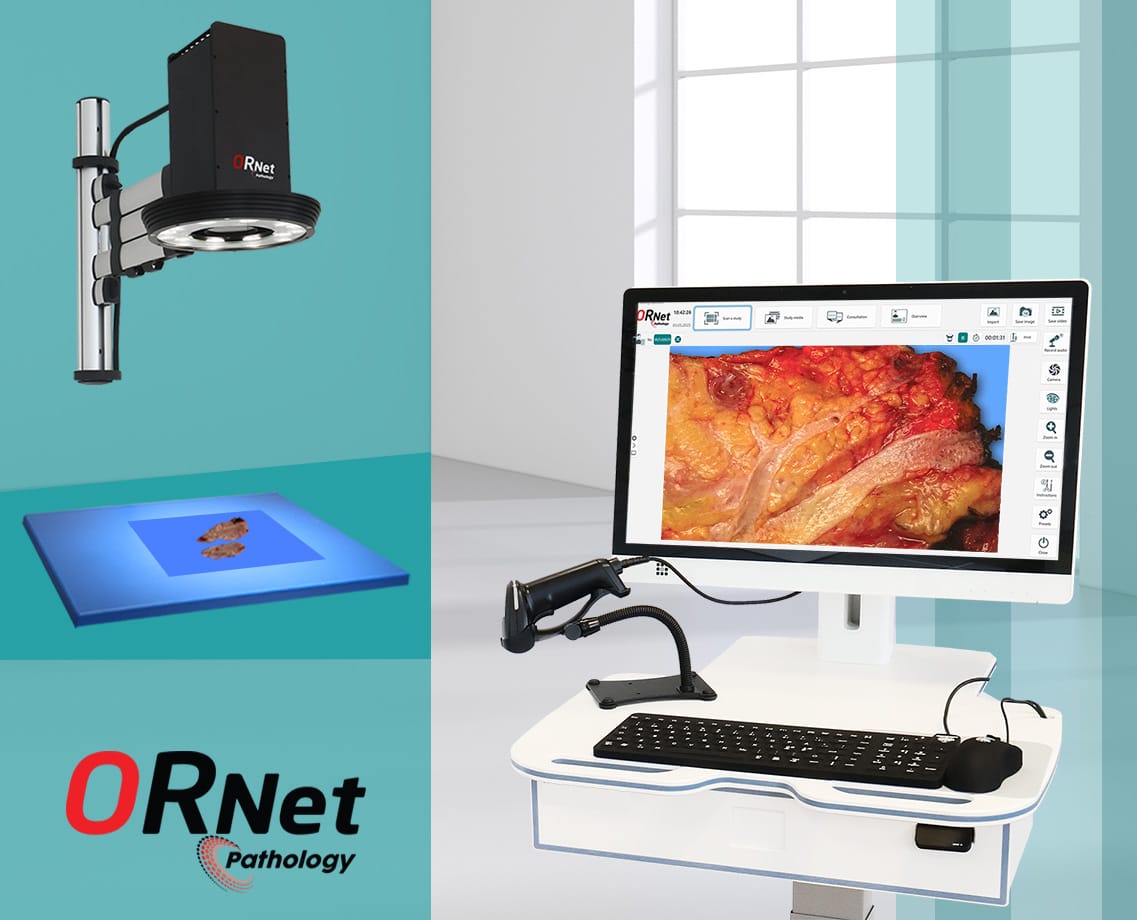
Use of ORNet Pathology to Achieve Backward Traceability
Another simpler and better way to achieve backward traceability for medical samples is to implement a comprehensive & centralized management system for pathology labs; ORNet Pathology.
ORNet Pathology offers a variety of features from containers and cassette verifications using barcodes to documenting samples using images and videos. All the files are tagged with patient and procedure information for enhanced traceability. Furthermore, the system is integrated with LIS/PACS Archives and all files are available for viewing at any time.
Additionally, the system offers a variety of features that assist pathologists and biomedical scientists during the workflow and make it simple, efficient, and secure.

Click here for more information about our solution or use the Kontakt os form to talk to our team and get personalized information.
Conclusion
Achieving backwards traceability of medical samples is crucial for ensuring patient safety, improving laboratory processes, and complying with regulations. By developing clear protocols, standardizing record keeping, and implementing a laboratory information system, laboratories can achieve efficient and accurate tracking of samples. As an alternative, labs can use tools such as ORNet Pathology to achieve backward traceability and much more while overcoming challenges such as cost, training, and data management.



One thought on “Backward Traceability of Medical Samples: Why It Matters and How to Do It”
Comments are closed.