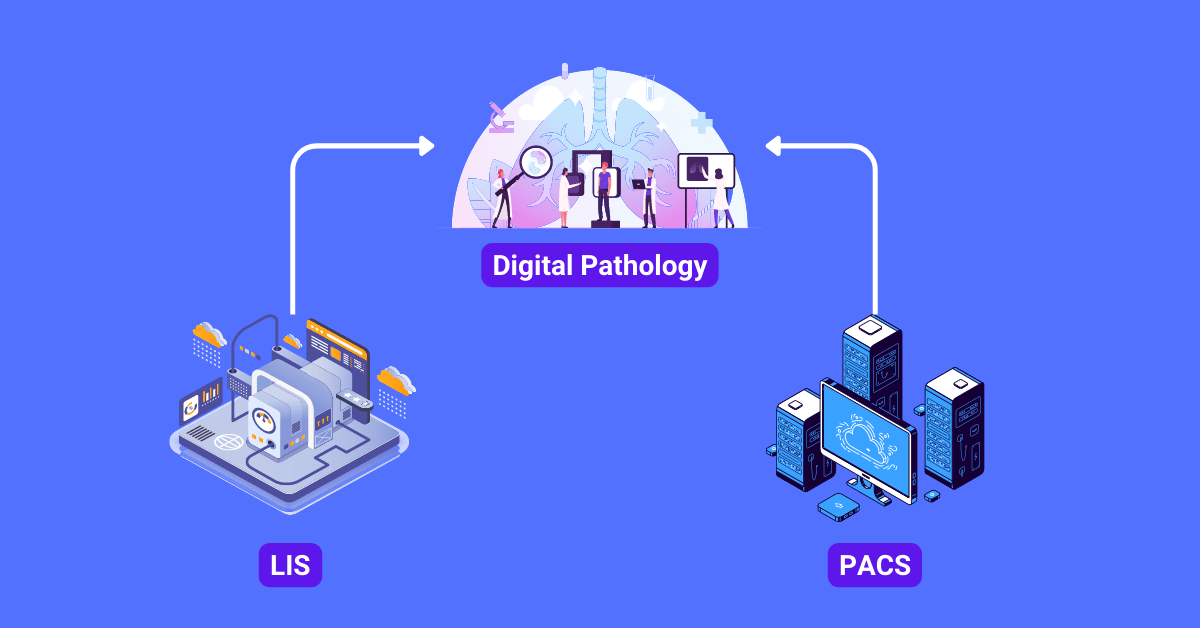
Digital pathology has greatly enhanced the way we diagnose disease.
By digitizing pathology slides and using advanced imaging technologies, pathologists can now get a more detailed and accurate view of tissue samples. This has led to improved accuracy of diagnoses, faster turnaround times, and enhanced collaboration between pathologists and other healthcare professionals.
Two critical components in this transformation are Laboratory Information Systems (LIS) and Picture Archiving and Communication Systems (PACS).
In this article, we will take a closer look at LIS and PACS integration in digital pathology. We will discuss the benefits of this integration, the challenges that need to be addressed
What are LIS and PACS?
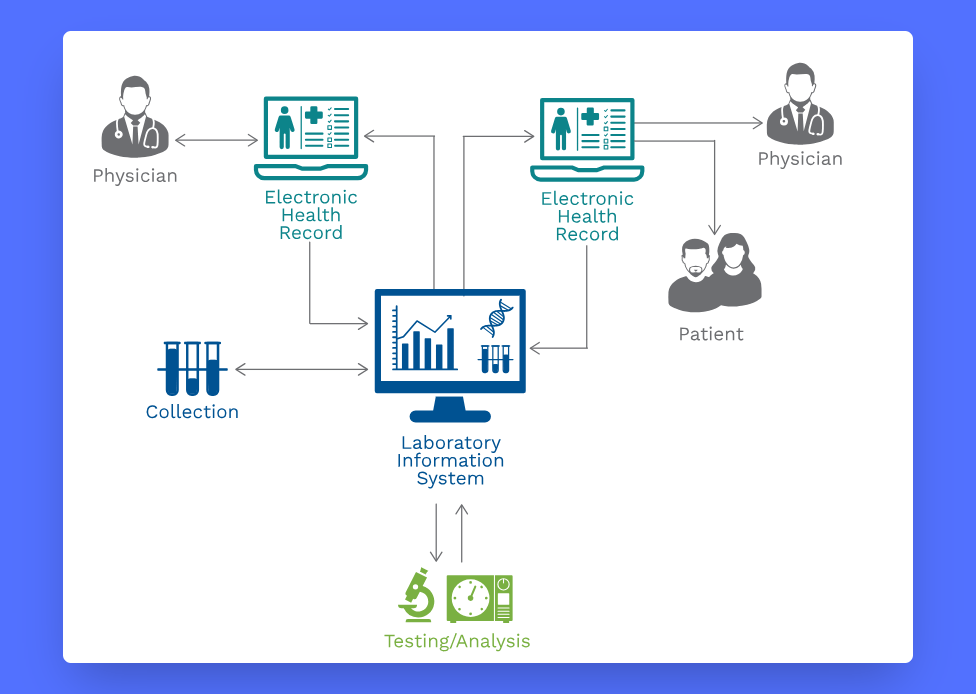
Laboratory Information Systems (LIS)
LIS is a software system that records, manages, and stores data for clinical laboratories. It’s a highly configurable application that can manage patient data, integrate instruments, automate workflows, and enforce rules for verifying and releasing test results.
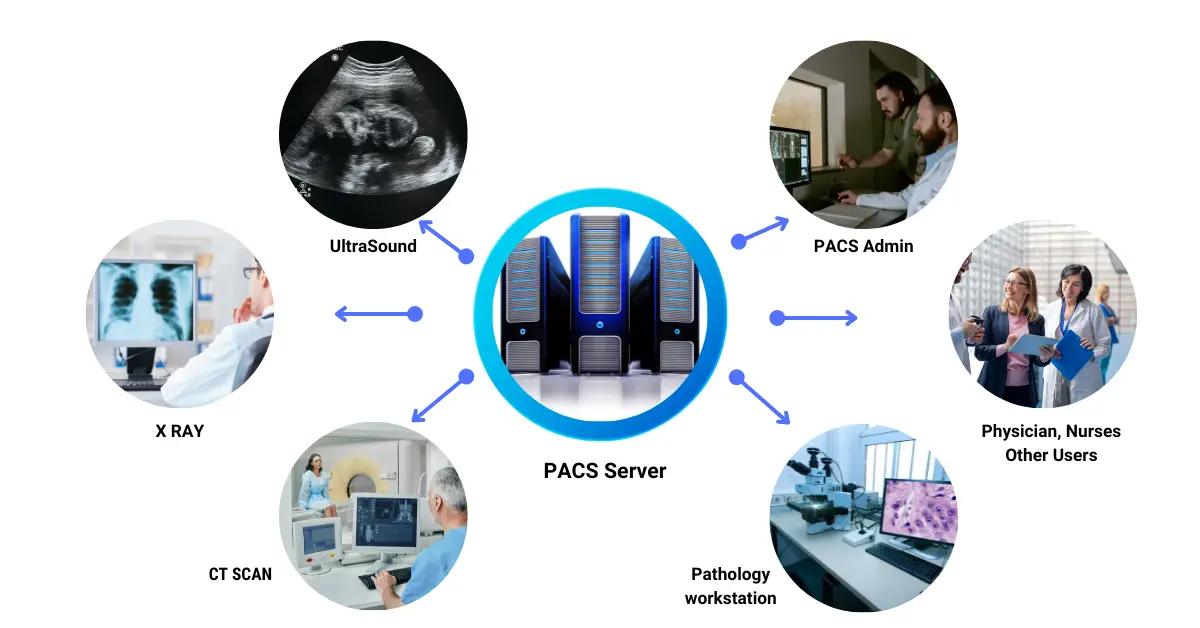
Picture Archiving and Communication Systems (PACS)
PACS, on the other hand, is a medical imaging technology that provides storage, retrieval, and access to images from various medical imaging modalities. It allows for the secure and efficient sharing of images among healthcare providers. Essentially, PACS replaces hard-copy-based means of managing medical images, such as film archives, with digital archives.
Advantages of LIS & PACS in Digital Pathology
The integration of Laboratory Information Systems (LIS) and Picture Archiving and Communication Systems (PACS) plays a pivotal role in the field of digital pathology. These systems, when integrated, offer numerous benefits for all stakeholders.
Here are some of the key benefits:
1. Streamlined Workflow
In digital pathology, LIS automates the data entry process, eliminating the need for manual transcription of patient information. Similarly, PACS allows the automated transfer and storage of pathology images. The seamless integration of these two systems allows for efficient management and retrieval of digital pathology images and patient information. Pathologists can access both the patient’s clinical data and their digital slides in one place, making the process more streamlined.
2. Enhanced Diagnostic Accuracy
By integrating LIS and PACS, pathologists have access to complete patient data, including medical history, previous test results, and images. This comprehensive information enhances the accuracy of diagnoses and treatment decisions. They can easily compare current images with previous ones, track changes, and correlate this with the patient’s clinical history.
3. Improved Patient Care
Faster and more accurate diagnoses mean that patients can receive appropriate treatment sooner. This can significantly improve patient outcomes, especially in cases where early intervention is critical.
4. Improved Turnaround Time
LIS & PACS integration helps expedite the analysis and reporting process by eliminating manual tasks and automating result delivery. Pathologists can efficiently review and finalize reports, leading to faster turnaround times and quicker patient management.
5. Consultation / Collaboration
Another key advantage of LIS and PACS integration in digital pathology is that it enables seamless collaboration between pathologists, lab technicians, and other healthcare professionals involved in the patient’s care.
They can easily access and share pathology reports, images, and annotations, leading to better communication and coordination.PACS integration facilitates collaboration among pathologists and other healthcare professionals. Pathology images can be securely shared and accessed remotely, enabling consultations and second opinions from experts worldwide. This promotes interdisciplinary collaboration and improves patient care outcomes
6. Research and Education:
In the past, pathologists had to rely on paper records and physical slides to conduct research and train new pathologists. However, with the integration of LIS and PACS, pathologists can now access and analyze large datasets of digital pathology images and patient data with ease. This allows them to conduct more complex and sophisticated research that can lead to new discoveries and improved diagnostic techniques.
In addition, Data from LIS and PACS can be used to create comprehensive training materials for future pathologists. Gross images, digital slides, and patient data can be used to create interactive learning modules that can improve the overall learning experience. This is a much more effective way to train pathologists than the traditional methods.
Challenges & Considerations
While LIS & PACS integration brings numerous benefits to digital pathology, there are also challenges and considerations that need to be addressed:
Data Security: Perhaps one of the biggest challenges that digitalization has brought us is data security. With the integration of LIS and PACS, it is vital to prioritize data security and patient privacy. Robust security measures and access controls must be in place to protect sensitive patient data and pathology images. Compliance with regulatory standards, such as HIPAA, is fundamental.
Cost Consideration: Another important aspect to consider for hospitals and labs is cost. LIS & PACS integration may involve upfront costs for software, hardware, and infrastructure upgrades. Therefore, it is important to evaluate the return on investment and assess the long-term benefits before committing to integration.
Training & Support: Adequate training and support for pathologists and laboratory staff are essential when implementing LIS & PACS integration. Education and familiarization with the integrated system ensure proper utilization of its features and maximize the benefits.
Concluding Thoughts
In conclusion, the integration of PACS and LIS plays a crucial role in the field of digital pathology. It improves efficiency, allows for centralized storage and retrieval of pathology images and patient information, and facilitates collaboration among healthcare professionals. However, careful consideration of compatibility, data security, and training is necessary to ensure successful integration and optimize its benefits.